

 Actually those shows made me super impressed in the past until one fine day i found out that there's alot of Computer editing involved. Why don't such '威风' martial arts exist? D:
Actually those shows made me super impressed in the past until one fine day i found out that there's alot of Computer editing involved. Why don't such '威风' martial arts exist? D:
Let's start on this chapter for real.
Internal energy: is the total energy of particles comprising of Kinetic energy and potential energy.
Kinetic compound: Due to vibrations, directly related to temperature.
Potential compound: Due to stretching and compressing of bonds, related to distance of particles.

Melting: Change of state from solid to liquid. For a pure substance, the degree of melting is at a definate temperature known as the melting point.
The melting point of ice into water is 0 degrees and during the change of state, there is no change in temperature.
Now everyone please watch this video D: Don't worry, it only takes less than 30 seconds, It's so traumatizing to see one big chunk of ice caps melting and falling into the sea like how we pour flour to bake our cakes. Must watch k. :]
This is a real life example of melting. &I don't know how i should be reacting. D:
 This is seriously beautiful leh D: i just searched 'Freezing' in google and this caught my attention. @*#()!^ Pretty.
This is seriously beautiful leh D: i just searched 'Freezing' in google and this caught my attention. @*#()!^ Pretty.Boiling: It is when a pure liquid changes into water vapour at a fixed or constant temperature, which is also known as the boiling point.
Condensation: It is when water vapour is cooled at a fixed or constant temperature. Thermal energy is given out during this process.
How do we determine the boiling/condenstation point? Answer: Heat/cool the water until there's a change. Like for boiling, heat until the water boils and that is the boiling/condensation point.
When the intermolecular forces break and the molecules can move more freely, we can say the state of liquid has changed to gas.
Evaporation :}
EH! I didn't know evaporation causes the cooling that we feel after being out of the pool. I thought it was the stupid wind. (@#@#(* =.=
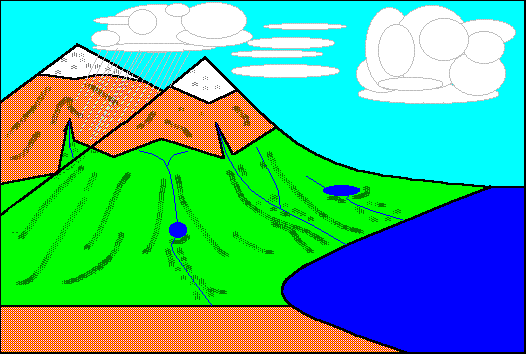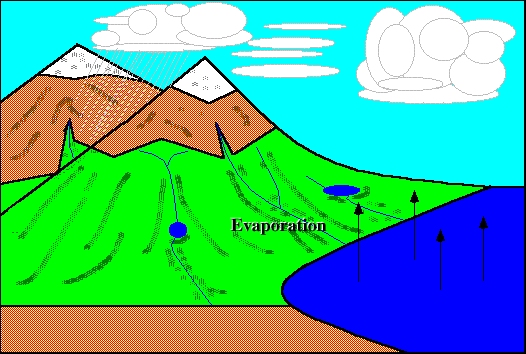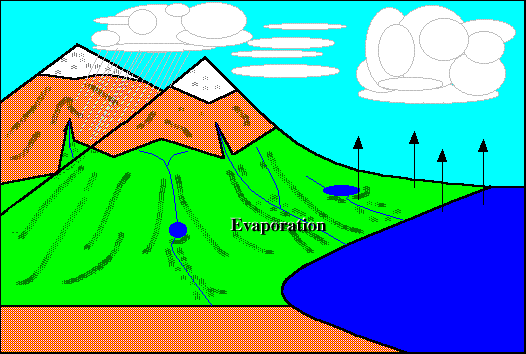 Very creative picture done by just by using 'paint' :D Still got animation somemore!
Very creative picture done by just by using 'paint' :D Still got animation somemore!
Differences of Boiling and evaporation:
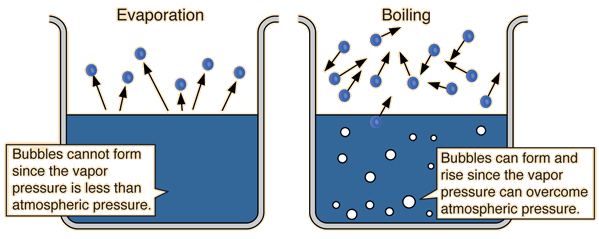
Difference #1 : Boiling occurs at a fixed temperature while evaporation occurs at any temperature. (You can think of it logically, like imagining your clothes can only dry at 28.976 degrees, that's of course impossible:)
Difference #2: Boiling is a quick process while evaporation is a slow process. (If boiling was a slow process, how long would chemistry practical lessons take? :)
Difference #3: Boiling takes place throughout the liquid while evaporation takes place only at the liquid surface.
Difference #4: Boiling forms bubbles while evaporation do not.
Difference #5: Temperature remains constant for boiling while temperature varies for evaporation.
Difference 6: Thermal energy must be supplied an energy souce for boiling to take place while evaporation can take place on it's own due to the thermal energy supplied by the surroundings.
How does evaporation occur?
It occurs when the more energetic molecules overcome the downward attractive forces of other molecules and escape, carrying thermal energy with it.
Factors affecting the rate of evaporation:
1. Temperature: The higher the temp, the faster a liquid evaporates due to the larger amount of energetic molecules running away from home :)
2. Humidity: The higher the humidity, the lower the rate of evaporation.
3. Surface area of a liquid:If the liquid has a bigger surface area, the rate of evaporation would be faster:)
4. The movemen tof air: The rate of evaporation is faster in moving air than in still air. I think that's why it's cooler with the fan/aircon right? (:
5. Pressure: The lower the atmospheric pressure, the higher the rate of evaporation
6. Boiling point of land: Liquids with lower boiling points will evaporate faster.
Hehe. Now for the Applications of evaporation:
1. When you're having a fever, a wet and cold towel will leave a cooling effect on your forehead when it evaporates, keeping down the temperature :)
2. Cooling effect on your skin after applying perfume/When your perspiration evaporates.
3. Refridgerator uses the principals of condenstation and evaporation:)
4. Clothes dry due to evaporation :)
That's all for lessons forever and ever and ever D:
But i'll still be posting one more to share my thoughts :D
Labels: Chapter Nine